All rights reserved - Copyright
( The english version is incomplet and translated by software and not yet corrected . Sorry .
French version is better . )
From 1990 2003 have, load of course in Calculee Image has
IPT Universite Paris 8 [Owner of the course].
(For students of deug in Visual arts, etc…)
End of the page.
(to be able to change heading for without frames).

COLORIMETRY
(Concept of colorimetry for Calculee Image)

Paragraphs of this page:
- Light and Color.
- Principle of definition.
- Space colouring.
- File image and code color.
- Basic change.
- Modeling of the light.
- LIGHT AND COLOR.
Newton emitted the corpuscular theory of the light,
Huygens A creates an undulatory theory of the light,
Maxwell has builds an electromagnetic theory to him.
Lastly, Louis de Broglie A proposes the wave mechanics
while succeeding has to reconcile the duality wave-corpuscle.
The light results from the feeling produced by
the electromagnetic waves in a spectral field going from 380 nanometers has 780 nanometers.
This band is appelee “spectrum visible”.
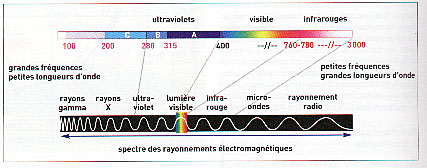
Each wavelength corresponds has a perceptive feeling appelee “color”.
In the order decreasing wavelengths, the denominations are :
red, yellow, green, cyan, blue, purple
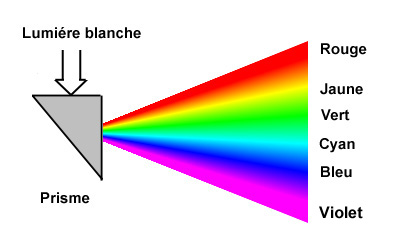
The color is provoquee by the light which our eyes collect,
but it nait - and did not nait only in our brain.
THE COLOR EAST A PERCEPTION OF THE BRAIN.
The white color is made up of the colors of the spectrum.
The color of an object corresponds to the wavelength that
this object considered or transmitted; because the other rays of the white light are absorb.
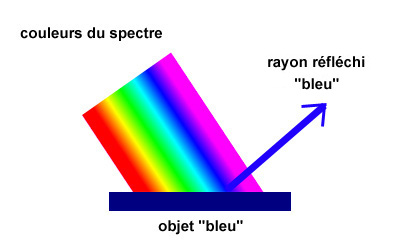
How is a color in image calculee made (data-processing image)?
-
PRINCIPLE OF DEFINITION
.
To make color in image calculee, 2 factors are needed:
- It is necessary to have a base.
- A quantification should be made.
- First factor :
A BASE.
Definition:
A base is a finished whole of elements which have the following properties:
- All the colors are a combination of the elements of the base.
- No element of the base can be a combination of the other elements of the base
(independence).
There are 2 basic kinds:
- a base made up of colors.
- a base made up of attributes psychovisuels.
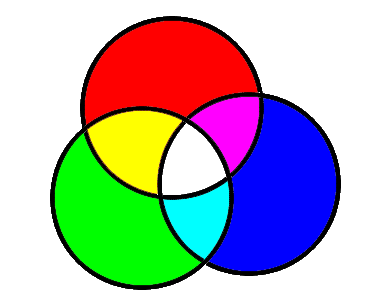
a°) _ A base of 3 colors (three-colour process) :
- base additive (additive synthesis):
< Red Green Bleu> or (R G B)
- base subtractive (syntheses subtractive):
< Cyan Magenta Yellow> or (C M J)
- Quadrichromy :
base subtractive particuliere (second property of the base not checks) :
( C M J K).
As one mixture 3 chemicals, in equal proportion, of colors
: cyan, magenta and yellow. One obtains a gray color instead of black;
this is with the physicochemical properties of the products.
This is why the black is added.
Note:
Mixture subtractive :
one withdraws white light (RVB) the color complementary to the color of the filter.
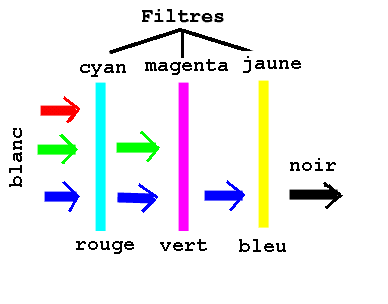 Application:
Application:
- R V B---------------- monitor, scanner, shooting, video-projector.
- C M J --------------- printing, printer.
- Quadrichromy ---- printing, flasheuse.
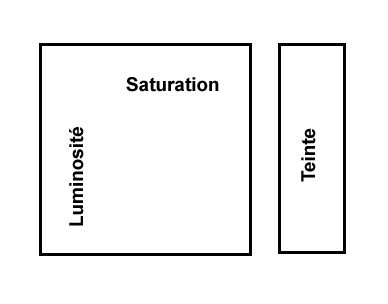
b°) _ a base of 3 attributes psychovisuels:
< Teinte Saturation Luminosity> or (T S L)
- The colour is an attribute which describes a pure color immediately,
like the red pure, blue pure, etc dyes It defines the color itself.
- Saturation is an attribute which describes the deterioration of a
pure color with the white or a level of gray.
It measures the proportion of pure color compared to the white.
It represents the factor of purity of the color.
This concept makes it possible to distinguish it pink from the red.
- The luminosity (intensity, nuance) is an attribute which qualifies
the luminosity of a color. The luminosity given light intensity emitted by the color
(clear or sunk color).
- Second factor :
THE QUANTIFICATION:
System of measurement of the elements of the base.
This measurement depends on the representation of the elements.
In general, one uses a byte to code this measurement,
thus it varis of 0 A 255.
One thus uses a word of 24 bits to code a color.
In this case, the number of possible colors is :
255*255*255 = 16.777.216. (or: 224 = 16.777.216)
Proposal:
A color can be exprimee by 3 numerical values.
That is to say the additive base:
{Red Blue Green}
vector color = r * Red + g * Green + b * Blue = (r g b)
r, g, b are 3 numbers (scalar).
Examples in three-colour process:
Red Green Bleu ---- Color obtained.
000.000.000 ----------- black
255.255.255 ----------- white
255.000.000 ----------- red clear
128.000.000 ----------- red sinks
255.255.000 ----------- yellow clear
128.128.000 ----------- yellow sinks
etc ...
Yahoo! GeoCities cubic color
(colors with their numerical values into hexadecimal and decimal).
Proposal:
That is to say the additive base: {Red Blue Green}.
A color is exprimee by the 3 intensities of the 3 colors of the base.
The basic colors additive, they are called also primary educations, primitives.
Definition:
Two colors are “complementary”, if their linear combination gives the white color.
Proposal 1:
The complement of a color is the white minus this color.
Proposal 2:
By mixing 2 of the 3 primitives, one obtains the color complementary to the third primitive.
Proposal 3:
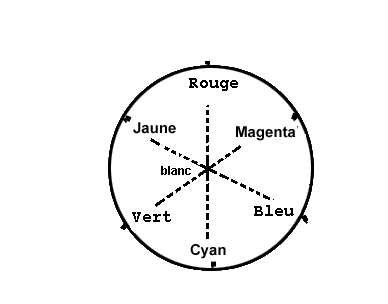
In the chromatic circle.
Two complementary colors, if they are diametrically opposite.
Corollary:
In the chromatic circle. One a:
- the red and the cyan are complementary;
- the green and the mangenta are complementary;
- blue and the yellow are complementary.
- SPACE COLOURING.
Chart of the colors.
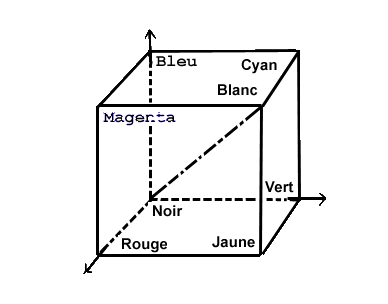
- Space 3D:
- R G B and C M J (cubic of the colors):
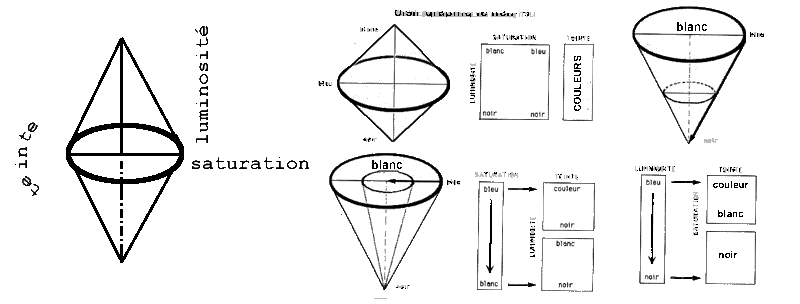
- T S L (double cone or cylinder).
- Space 2D:
The charts 2D are usable to choose the colors.
* R V B and C MR. J:
- Chromatic Circle:
- The graph of C.I.E. (Internationnale Commission of Lighting).
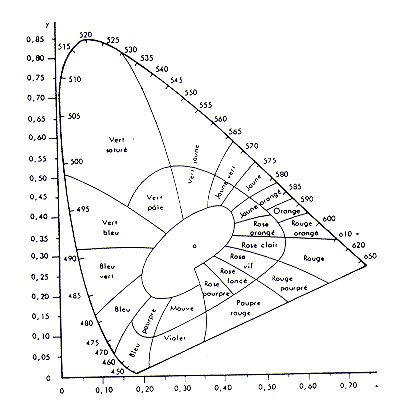
(graph extracted the article :
Introduction to colorimetry, of Michel HENRI)
* T S L (2 tables):
All the colors are not representees there at the same time on the tables.
- LUTE (Look Up Table):
A table (pallet) of the colors. Colors indexees.
In general, one uses a byte to code the address, thus one will have 256 boxes;
as one puts a color by box; thus there will be 256 possible colors.
On the other hand, contents,
i.e. the color, one can code it with a word of 24 bits.
It will be said that one has 256 displayable colors sumultanement parmis more than 16 million.
- Nuanciers (Pantone).
A catalogue of sample of the preset colors. Samplings of the printed colors,
identifiees by a reference chiffree.
- FILES IMAGES AND CODES COLORS.
The definition of an image, it is the number of lines per a number of columns.
The definition is measured in a number of points on the total surface of the image.
The resolution of the image is the number of points (pixels) per unit of length (inch).
The outline, mesuree in lines of points per inch.
Pixel (Picture Element), the elementary point constituting the image.
dpi (dowry per inch) = a number of points which can be juxtapose on an inch (2.54 cm).
The size (the poid) of the image is related to its definition (dimension),
of its resolution (squares it), of its nature (code color).
More one wants color and of smoothness (screen), and more the resolution must be high.
Contrast expresses the distribution of the ton clear, average and sink.
- BASIC CHANGE.
- R V B and T S L
- 1e formulation:
T = arcsin [(3/2) 1/2 * (V - R)/S]
S = (R2 + V2 + B2 - R * V - B * R - V * B) 1/2
L = (R + V + B)/3
R = 1 - (1/3) * S * cos (T) - (1/31/2) * S * sin (T)
V = 1 + (2/3) * cos (T)
B = 1 - 1/3 * S * cos (T) + 1/31/2 * S * sin (T)
- 2nd formulation:
T = (1/360) * {90 - Arctan [(2 * R - V - B)/(31/2 * (V - B))] + X}
with: X = 0 if V > B
with: X = 180 if V < B="">
S = 1 - {(1/I) * [min (R, V, B)]}
S = 1 - { ( 1 / I ) * [ min (R , V , B ) ] }
or
S = (R2 + V2 + B2 - R * V - R * B - B * V) 1/2
I = (1/3) * (R + V + B)
- 3rd formulation of Nicolas Holzschuch:
max = max (R, G, B)
min = min (R, G, B)
V = max
S = (max - min)/max
delta = max - min
If max = R Then H = (G - B)/delta
If not If max = G Then H = 2 + (B - R)/delta
If not If max = B Then H = 4 + (R - G)/delta
H = H * 60
If H < 0="" Alors="" H="H">
- 4th formulation has “telesun.insa-lyon.fr”:
- 4e formulation a "telesun.insa-lyon.fr" :
To pass from the initial representation (RVB) to this representation, one operates in the following way:
With = U1* (has log (R) + B log (V) + C log (B))
C1 = U2 (log (R) - log (V))
C2 = U3 (log (B) - 0.5 log (R) - 0.5 log (V))
U1, U2 and U3 are factors of standardization.
(has, B, c) depends on the authors. Enough running: (has, B, c) = (0.612, 0.369, 0.019)
Then passage of AC1C2 with HLS by
L = A
S = (C12+C22) 1/2
H = arcos (C1/S)
- R V B and C MR. J
R = 1 - C
V = 1 - M
B = 1 - J
- CMYK:
K = min (C, M, Y)
C = C - K
M = M - K
Y = Y - K
Proposal:
Any image color can be converted into an image in levels of gray by simple addition of the primary colours.
The formula has to employ is as follows:
grey = (0.30 * red) + (0.59 * green) + (0.11 * blue)
- Note:: the formula is not single.
- MODELING OF THE LIGHT.
Light = Ambient + Reflexion + Refraction
Total reflexion = reflexion diffuses + specular reflexion
- Le dossier couleur
de la revue Pour la Science .
- Le site de Delphine BOURGEOIS sur la
Couleur .
- Le site de
Nicolas Holzschuch
sur la colorimetrie .
- Le site de Jean-Christophe SEKINGER :
Contribution au Traité des couleurs de Goethe .
- Le site sur les Couleurs (echo productions) .
- Bases de la colorimetrie
sur le site du Ministere de la culture .
- La lumiere sur le site pyrotechnique.net .
(site pyrotechnique.net) .
- Comment representer les couleurs
Universite Lyon 1
.
- Le site a
( telesun.insa-lyon.fr ) sur la colorimetrie .
- Le site de la Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage .
- Dictionnaire Chromatique .
CALLET Patrick.
Couleur-lumiere, Couleur-matiere.
Editions Diderot, 1998.
Beginning of the page………. Return behind
Francais
English
Francais

English









